
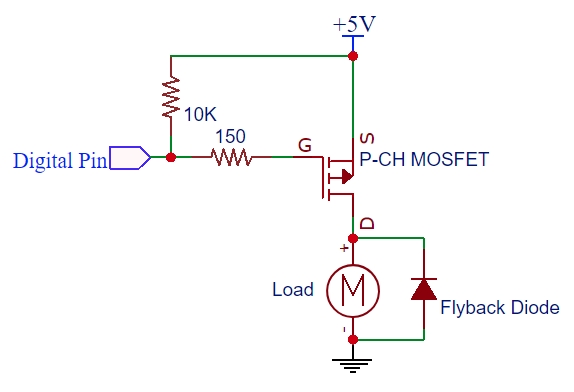
Once the input voltage is LOW then P-channel MOSFET connected in the circuit will be turned ON & N channel MOSFET will be turned off because its gate to source junction is biased negatively as a result the motor in the circuit turns in one direction. In this circuit, these two MOSFETs are simply connected to generate a bi-directional switch using a dual supply through the motor connected in between the common drain & GND reference. This switch circuit uses two MOSFETs like the P channel and the N channel to control the motor in both directions.

The complementary MOSFET switch circuit for controlling the motor is shown below.
At last, the gate & the drain will stay at the negative polarity while the source remains at the ‘0’ value. So, by variations of the region’s voltage values, the flow of current gets controlled. The depletion layer’s region width will affect the conductivity value of the channel. This region mainly depends on the layer concentration formed because of the holes. In this condition, once a drain is reverse biased then the device begins conducting although, when the negative voltage within the drain is enhanced then it results in the depletion layer formation. Once the negative (-) voltage is applied at the gate terminal then the minority charge carriers like electrons in the n-type get attracted towards the p-type channel. The channel in this MOSFET is pre-build because of the available p-type impurities in it. The p channel depletion MOSFET construction is reversed to n channel depletion MOSFET. When the hole concentration forms the channel & the flow of current throughout the channel gets improved because of an increase within negative gate voltage, so this is known as P – Channel Enhancement MOSFET. Thus the current flow from the source to the drain can be controlled through the voltage applied at the gate terminal so MOSFET is known as a voltage-controlled device. Here, the resistance of the channel mainly depends on the side view of the channel & again this channel’s cross-section depends on the negative voltage applied at the gate terminal. The channel formed within the MOSFET provides resistance to the flow of current from source to drain. When a negative voltage is applied at the drain terminal then negative voltage within the drain region decreases the voltage difference between gate & drain decreases, thus, the conductive channel width gets decreased toward the drain region, and current supplies from source to drain. The electrons available at the n substrate because of the repulsive forces will get moved. When a negative voltage is applied to the gate (G) terminal then the +ve concentration of the charges will be settled under the dielectric layer due to the capacitance effect.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
